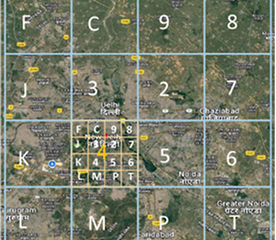
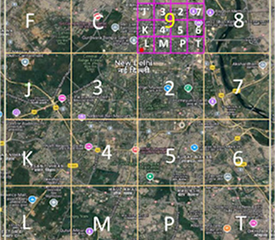
1. A bounding box that covers the whole country is employed.
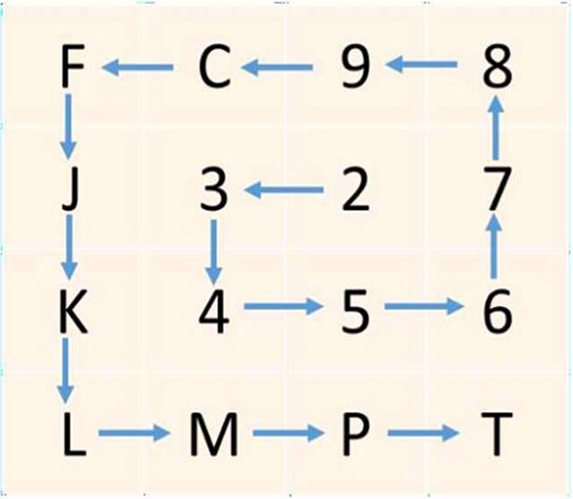
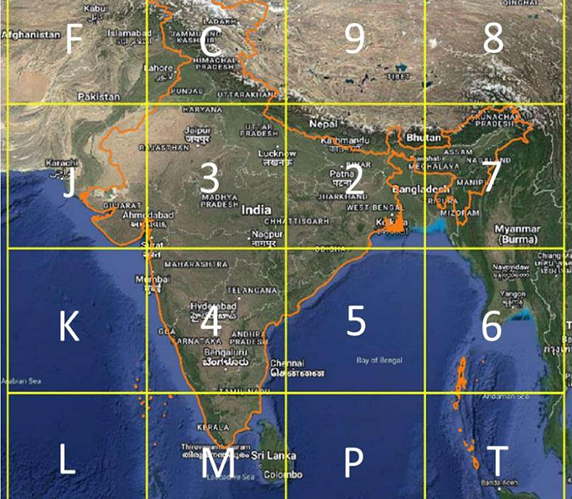
2. Level-1 Partition: The bounding box is divided into 16 areas, each 4x4. One of the 16 symbols marks each area. The first letter in the code tells you which of these areas it is.
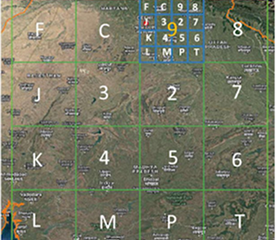
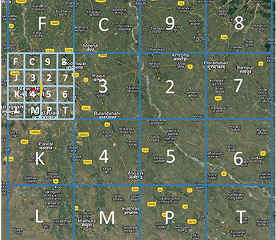
3. Level-2 Partition: Each zone is then split into 16 smaller parts in the same way. The second character tells you what the subregion is, which makes 162 = 256 subregions.
4. Successive Levels: The encoding goes on for 8 more levels in the same way. The 10-symbol code points to one of the 1610 cells in the bounding box.